AWS S3 storage has automatically data transportation mode known as Storage Classes for cloud storage objects defines availability and pricing model, you can select a default storage class for a bucket while creating it, all the objects added to the bucket will inherit this storage class. If you do not choose any storage class while creating a bucket it will be set to storage class Standard storage, you can also change the storage class of an already existing object by changing the object life cycle rules, what’s standard storage…. object life cycle rules? well let’s understand all the available storage classes first and then life cycle rules.
Available Storage Classes in Google Cloud Storage
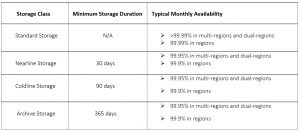
Minimum Storage Duration is what you will be charged for even if you delete , replace or move the object to a different storage class .
Availability relates to the time that the data center is accessible or delivers the intend service, its measured by overall service downtime.
All the storage classes provide the following, unlimited storage, worldwide accessibility and worldwide storage locations, Low latency , High durability (99.999999999% annual durability), Geo-redundancy(only if the data is stored in a multi-region or dual-region) and a similar experience with Cloud Storage features, security, tools, and APIs.
Standard Storage
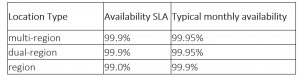
it’s s the best storage class for data which is frequently accessed and/or stored for only short periods of time, when used in Regional Locations standard storage is good for storing data in the same location for co-locating the resources such as Google Kubernetes Engine clusters , which helps you in maximizing performance and reducing network charges, and single Regional storage provides an availability SLA 99.9%. for dual-region and multi region storages google cloud provides an availability SLA >99.95% where Dual-Region enables you to get optimized performance when accessing Google Cloud products that are located in one of the associated regions, and a Multi- Region is good for storing data that is accessed from many locations in the world .
you can select Location Type while creating a bucket.
Nearline Storage
It’s is a low cost and highly available and durable storage service for storing infrequently accessed data it is better to chose Nearline Storage where you can afford lower availability compared to Standard Storage, this storage class is ideal for data that you plan to read or modify once per month or less, for example: if you want to add files to cloud storage continuously and want to access the files once a month for analysis then Nearline will be much better choice.
Availability of Nearline Storage data is as follows
Coldline Storage
This storage class is ideal for data you plan to read or modify at most once a quarter, it provides a very-low-cost, highly durable storage service for storing infrequently accessed data it has a 90-day minimum storage duration and higher costs for data retrieval compared to standard , availability of ColdLine Storage data is given below.

Archive Storage
It has the lowest-cost and good for data accessed once in a year or less, it can be used for online backup, and disaster recovery. even though the typical availability is comparable to Nearline Storage and Coldline Storage, Archive Storage has no availability SLA, and data is available within milliseconds which is much faster when compared other archive storage facilities in the market.
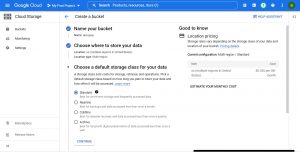
As mentioned, you can select default storage class while creating the bucket.
Object Life Cycle Management
Object Lifecycle Management is a feature of cloud storage that provides you with setting up Time to Live (TTL) for objects, automatically downgrading storage classes of objects after a certain period which helps you in managing costs.
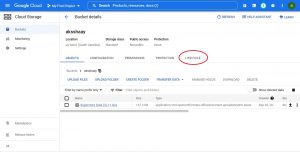
on your GCP web console go to the bucket on which you want to set object life cycle and select LIFECYCLE.
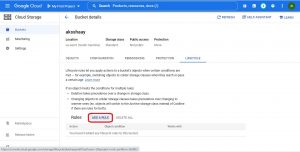
Click on ADD RULE
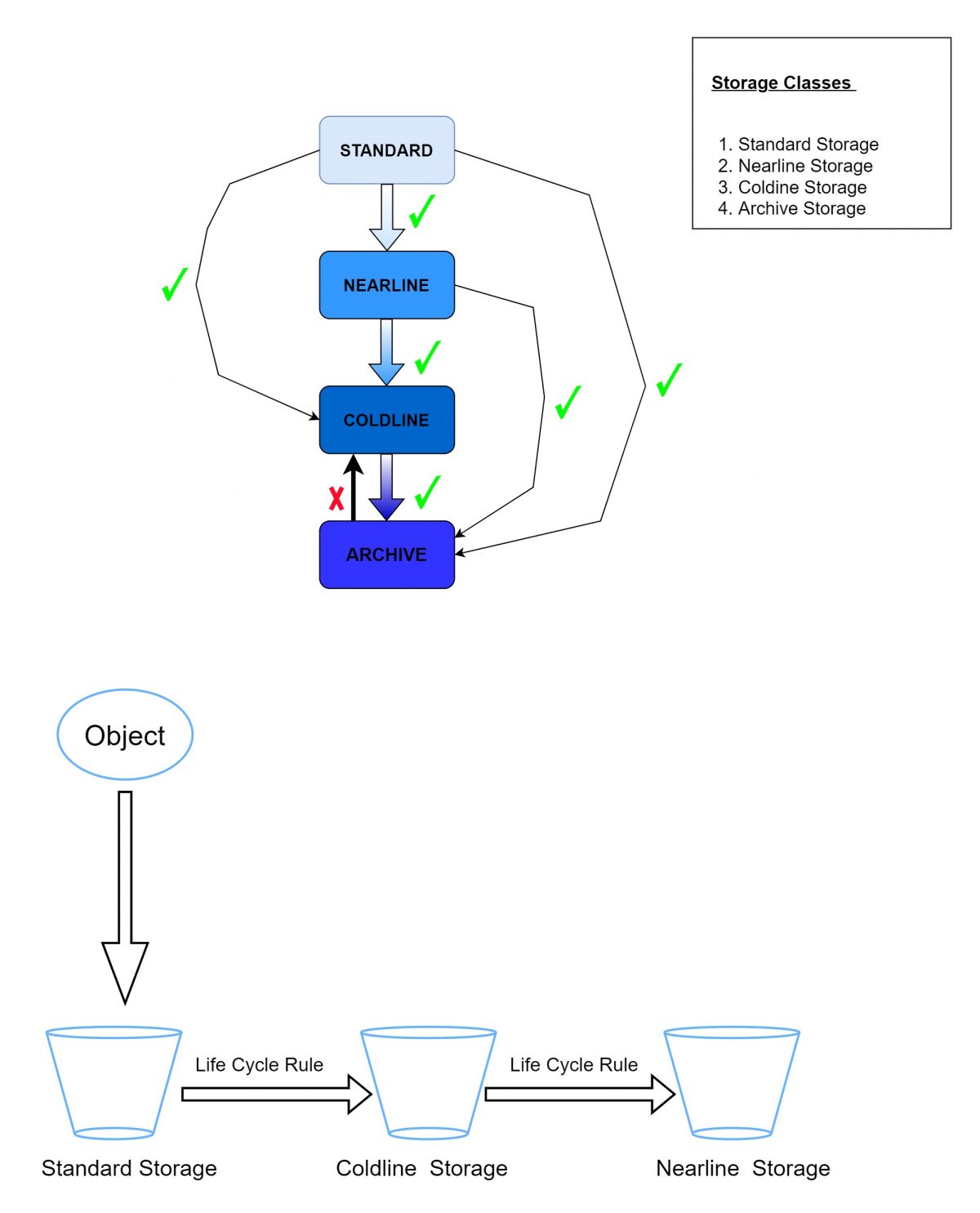
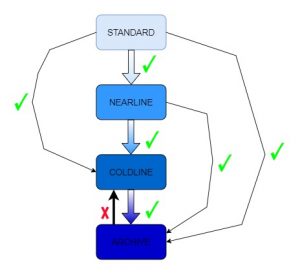
And then select a storage class storage class, and click on CREATE for object conditions .An object is transferred to a different storage class when it matches with any of the object conditions and if objects satisfies both the conditions it will be transferred to more colder storage (for example an object in standard storage matches both the conditions to be transferred in to Nearline and Coldline it will be transferred to Coldline)
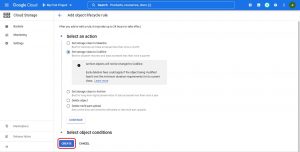
Note:while configuring object life cycle management you can only set a rule to transfer the object to a Colder storage class but not to a higher one.
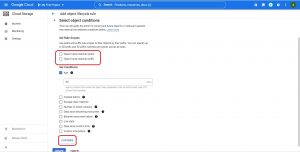
Select and set object condition as required.
you can select objects using Rule Scopes , for example suffix .jpg will select all the .jpg files in the bucket and applies furthers rules or actions on them, or a prefix log will select all the log files , you can also give path like example/aks , and then Set Conditions like age of the object , size of the object .
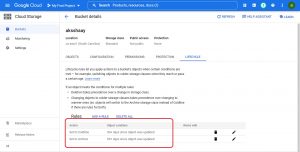
You can set as many rules you want , in the below given rule set will transfer all the files older than 29 days to coldline storage and files older than 89days to Archive Storage.
Please contact our team for any DevOps infrastructure management services website, LinkedIn