Git is open-source version control and source code management tool which allows us to efficiently track and manage code changes. Git is also key element in CICD pipeline automation for DevOps management.
Following are some basic commands to perform git operations from the terminal.
Important git commands
- How to install git.
sudo yum install git
- To check if git is installed, use the command below.
git --version
- To initialize git, go to your code’s directory and use the command below.
git init
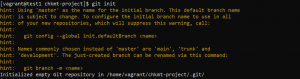
- Use the command below to configure git with your information for a git commit message.
git config --global user.name "your_username" git config --global user.email "your_email@example.com"
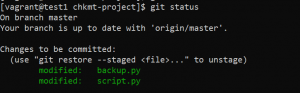
- For getting the status of our working directory and staging area use the following command.
git status

- Use the command below to add the file to the staging or index area.
git add 'filename'
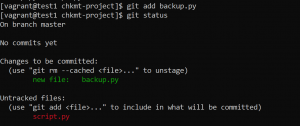
- With the git status command, we can see that the backup.py file has been added to the staging area while the script.py file is still untracked. To add it use the same command. To add all the files in a directory to the staging area at once use the following command.
git add .
- Use the following command to commit changes.
git commit -m "commit message"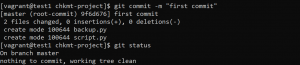
- Use the following command to update the last commit message. An edit window will open, edit your message and save it.
git commit --amend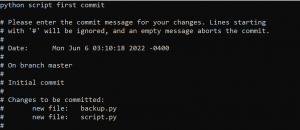
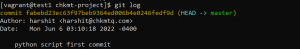
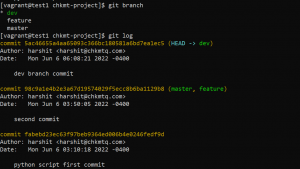
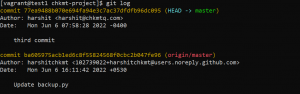
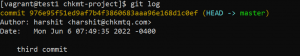
- To see commits done in the current branch use the following command.
git log
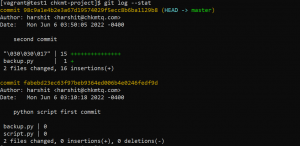
- Use the stat option with git log to get a summary of what was done to the committed files.
git log --stat
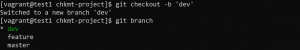
- To see which branch you are on, use the following command.
git branch

- To create a new branch use the following command.
git branch 'branch name'
- To list all branches use the following command.
git branch -a
- To go to another branch use the following command.
git checkout 'branchname'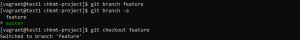

- To create a new branch from the parent branch you are currently working on with all changes from the parent branch use the following command.
git checkout -b 'branch name'
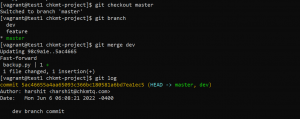
- For integrating different branches into a single branch use following command.
git merge 'branch you want to merge'
We have made changes in the dev branch and now want to integrate them into the main branch. So first we will checkout to the master branch and then use git merge.
- To delete a branch, use the following command.
git branch -d 'branch name'

- To add a remote repository, use the following command.
git remote add origin 'repository url'
- Use the following command to push code to a remote repository in the master branch. Enter username and auth token when prompted.
git branch -M master git push -u origin master

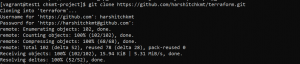
- To clone a remote repository use the following command.
git clone 'repository url'
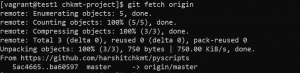
- To get the latest changes from the remote repo use the following command.
git fetch origin
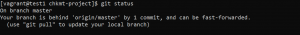
- To get the latest changes and integrate them into your working branch, use the following command.
git pull origin
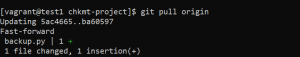
- To save uncommitted changes into a stack, use the following command.
git stash save 'message'
Here we have added line in our code but we don’t want to commit it and want to switch branch, in that case git stash is very useful.
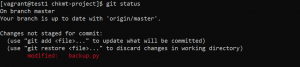
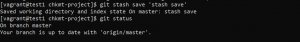
- Use the following command to list stash stack.
git stash list

- To bring back uncommitted changes saved at top of the stash stack use the following command.
git stash pop
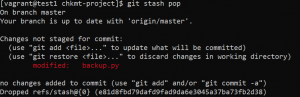
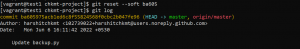
- Use the following command to reset a branch to the local committed code and remove all uncommitted modifications. It reset the head, working area, and staging area.
git reset --hard HEAD
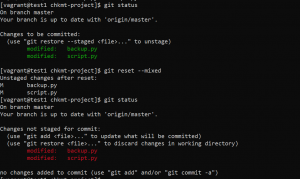
- Use the following command if you want to only reset the staging area and Head and not the working area.
git reset --mixed HEAD
- Use the following command if you want to only reset head.
git reset --soft HEAD
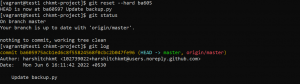
We have our head pointing to 976e95. We will use git reset and move head to point to ba605 but our changes will still be in the staging area.
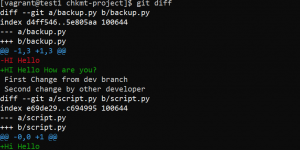
- To list the changes between the staging area and the current working directory use the following command.
git diff
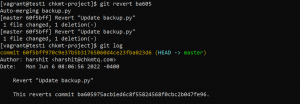
- To revert the committed changes and create a new commit with reversed content use the following command.
git revert HEAD
Please contact our technical consultants if you have anything related to source code management or DevOps pipeline automation to be discussed.