MySQL is one of the most used RDMS based database management systems based on SQL, it is a relational database stores data in tables in which data in tables may be related to each other these relations between tables helps to structure the data and preform operations like Create , Read, Update and Delete famously known as CRUD operations, In this blog let’s learn some MySQL commands.
How to use SELECT statement to get data from a MySQL table
MySQL select statement can be used to get data from one or more tables, you can get records of specific or all the fields of table using select statement, below is basic syntax of select statement
SELECT field1,field2 FROM table_name;
field1, field2 should be your tables column names, this gives specific columns/fields of the table, let us use select statement on below table “Persons”.

To get all the fields of a table use below command.
SELECT * FROM Persons;

MySQL select statement to get specific fields of a table.
To get specific fields from a table mention field names and table name, in the above snapshot you can see table “Persons” have five fields PersonID, LastName, FirstName, Address and City.
select PersonID,FirstName,City from Persons;
This command gives fields PersonID, FirstName, City from table named Persons.

MySQL select statement to get fields from more than one table.
How to use MySQL “ORDER BY” key word
ORDER BY is used to sort result in ascending or descending order, use ASC for ascending and DESC for descending, you can use this key word to sort integer or character fields.
Consider below table Persons to understand following syntax of ORDER BY.

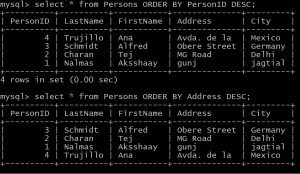
mysql> select * from Persons ORDER BY PersonID DESC; mysql> select * from Persons ORDER BY Address DESC;
above is the basic syntax for ORDER BY key word it gives all the field from table “Persons” and sorts PersonID in descending order and second command sorts Address field in DESC order.
How to use WHERE clause in MySQL commands
WHERE Clause is MySQL is used to filter the results, you can specify a condition to get the output according to your requirement, let us see an example using WHERE clause with SELECT statement on the below table named “Persons”.
Table Persons.

mysql> select * from Persons where City='delhi';
above command gives output from table Persons whose value for column City is delhi.

mysql> select PersonId,FirstName,City from Persons where PersonID>2;
above command gives fields of PersonId, FirstName, City whose PersonId is greater than 2.

How to use AND ,OR, NOT operators in MySQL commands.
you can use AND, OR operators along with WHERE clause, see below command to understand AND operator usage. consider table Employees for this.

mysql> select * from Employees where performance > 101 AND performance <105 ;
when you use AND operator a record will be displayed only if it satisfies all the conditions separated by AND operator, above command gives all the fields from table Employees whose value for performance is greater than 101 and less than 105 .

Now let’s see an example to understand how OR operator works, consider below table Persons for this.

mysql> select PersonId,FirstName,City from Persons where City = 'jagtial' OR City = 'Delhi' OR City = 'Mexico';
above commands gives details of persons from table Persons whose value for city is jagtial or Mexico.

How to use Between operator in MySQL
BETWEEN is a logical operator which you can use to specify a range to get a specific data, see below example to know how to use it, consider table Employees for this example.

mysql> select * from Employees where salary BETWEEN 40000 AND 50000;
This command gives all the rows from table Employees whose value for salary is between 40000 and 50000.

How to use LIMIT clause in MySQL
LIMIT clause is used to get specific number of records it used when working with large tables with thousands of rows because returning large data may impact performance, Let’s see how to use LIMIT clause .consider below table Persons for this
Table Persons

MySQL command to use LIMIT
mysql> select * from Persons LIMIT 3;
as you can see table Persons have 6 rows, above command gives only 3 rows as LIMIT given is 3.

How to add data to a table using INSERT statement in MySQL
INSERT statement is used to add data in a MySQL table , you can insert one row or multiple rows with a single query, and also you can add data to all the columns of a row or to specified columns of a rows.
syntax of insert statement
INSERT INTO table_name(field_name1,field_name2…) VALUES (value1,value2,value3..);
see the following example MySQL to understand how to use insert statement, let’s use table Persons for this.
Table Persons

check above given Persons table it has five fields, when you insert values to all the fields of a table you can do it directly without mentioning field names but when inserting values to specific fields you have to mention field names of the table, Let’s a example for each inserting values to all the fields of a table and specific fields of a table.
Inserting values to all the fields of a table.
mysql> INSERT INTO Persons VALUES (7,'Tej','Kiran','koramangala','banglore'),(8,'Patrik','Jhon','Madhapur','Hyderabad');
above command will add two new rows to table Persons.

Inserting values to specific fields of a table.
mysql> INSERT INTO Persons(PersonID,FirstName,City) Values (9,'williom','Gurgaon');
as mentioned above when you are adding values to specific columns of a table using INSERT statement you have to give field names, In above command I am inserting values to specific fields of the table Persons.

In the above snapshot observe 9th row values for last name and address are NULL (default value) as I inserted values into PersonID, FirstName and City only.
How to update a value in MySQL table using UPDATE statement
UPDATE statement in MySQL is used to modify existing data in tables, let’s make some updates to table Persons using UPDATE statement.
Table Persons

mysql> UPDATE Persons -> SET Address='Ejipura', City='Banglore' -> WHERE PersonID =1;
above command changes the values of Address and City of person with PersonID equal to 1, here Persons is table name and Address, City, PersonID are fields of the table.

you can aslo use UPDATE without WHERE clause , but use it only when you want update all the rows of that column.
mysql> UPDATE Persons -> SET City='Bangalore';
above command changes the value of City to Bangalore.

How to use JOIN clause in MySQL
MySQL JOINS are used to get data from multiple tables and combine the out put based on the related column the tables have, we have various types of joins in mysql INNER JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, LEFT JOIN, CROSS JOIN, below are two example tables Orders, CustomerDetails let’s use these tables to perform JOIN clause.
Table CustomerDetails

Table Orders

INNER JOIN
checkout above tables, I want list of customers who has ordered along with their orderID , inner join will do this for us as it gives all the records that have matching values in both the tables that means it searches for rows with common customerID from both tables and joins them.
mysql> SELECT customerName,orderID,orderDate -> FROM CustomerDetails -> INNER JOIN Orders -> ON CustomerDetails.customerID=Orders.customerID;

In above snapshot you can see I got customer names from CustomerDetails table for all the orders.
LEFT JOIN
Left join will return all the data from left table, and matching data from right table, let’s understand this with an example , I will use below tables to perform a Left join.
Table CustomerDetails

Table Orders

Problem statement: get order details of each customer , for this I should get all the customers from customerDetails table along with their order details from Orders table.
mysql> select CustomerDetails.customerID,customerName,orderID,orderDate -> FROM CustomerDetails -> LEFT JOIN Orders -> ON CustomerDetails.customerID=Orders.customerID -> ORDER BY customerName;
use tableName.columnName when you are accessing a common column from both tables, above command gives all the rows of customerID,customerName from CustomerDetais table and order details of each customer from Orders table.

RIGHT JOIN
MySQL RIGHT JOIN gives all the records from right table and matching records from the other table, see below example to understand this consider below tables for this.
Table CustomerDetails

Table Orders

Problem statement: Get all the order ID’s with customer name for each order.
mysql> SELECT orderID,orderDate,customerName -> FROM CustomerDetails -> RIGHT JOIN Orders -> ON CustomerDetails.customerID=Orders.customerID;
above command gives all the rows of orderID and orderDate from Orders table with customer name for each order, as as right join gives all the rows from right table and matching rows from left table.

How to use GROUP BY statement in MySQL
GROUP BY clause in MySQL is generally use with SELECT statement, it groups similar data from all rows to a summary column .
Table CustomerDetails

Problem statement: Get all the country names from where customers are located in.
mysql> SELECT country FROM CustomerDetails GROUP BY country;
above command will give each value of country column only once .

some aggregate functions like COUNT can also be used along with GROUP BY clause, see below example
Problem Statement: Get count of customers from each country.
mysql> SELECT country,COUNT(customerID) FROM CustomerDetails GROUP BY country;
above command gives count of customers from each country .

How to use INSERT INTO SELECT statement to add data to a table from another table.
sometimes you may need subset of a table or want to add data to a table from another table , INSERT INTO SELECT statement will allow us to do this, its simply SELECT columns from a table and INSERT INTO another.
Table CustomerDetails

Table mexicoCustomers(empty table)

I have table named “CustomerDetails”(given above) where I have customers from all countries and have another table named “mexicoCustomers” where I want have details of customers only from Mexico, in above given table we have only two rows of data you can manually insert this data but when you have thousands of rows it will be tough to do that, below is the command to do this.
mysql> INSERT INTO mexicoCustomers -> SELECT customerID,customerName,country -> FROM CustomerDetails -> WHERE country='mexico';
here mexicoCustomers, CustomerDetails are table names and customerID, customerName, country are fields of CustomerDetails , above command will select rows where country value is mexico from CustomerDetails and inserts it into mexicoCustomers.

Please contact with our technical consultants if you want to hire GCP cloud engineer to manage cloud infrastructure.


