Amazon Relational Database / Amazon RDS is a managed relational database service provided by AWS, aws will take care of hardware, management part , taking backups etc. it makes it easier to setup , operate and scale relational databases in the aws cloud, Some of its important features include Dashboard, Databases, Performance Insights and Snapshots for backup and disaster recovery , lower administrative burden , scalability , performance, advanced security , cost-effectiveness, higher availability.
The different Database engines that are supported by RDS are MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, Oracle, MariaDB, Amazon Aurora, Amazon RDS Custom.
Why Choose RDS over EC2 or on-premises setup
Elastic Compute Cloud (ec2) provides scalable compute capacity in the AWS cloud , amazon ec2 eliminates your need to invest in the hardware upfront so that you can develop and deploy applications faster and for a relational database in an on-premises server you need to take full responsibility for the server, operating system and database software for this you need to have dedicated teams for each task and for a database on an amazon ec2 instance amazon manages the layers below the operating system in this way amazon ec2 eliminates some of the burden of managing an on-premises database server , so it is a better solution than on -premises management, then why we need RDS ?
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) is a web service that makes it easy to set up, scale and operate relational database in the cloud. It provides cost efficient, scalable capacity for an industry-standard relational database and manages common database administration tasks , it frees you to focus on your application and your users, AWS itself suggest customers use RDS over ec2 for relational databases, below table gives you clear understanding why you should choose RDS over setting up databases on ec2 instances , Amazon RDS will manage every thing expect the application optimization.

Database Backup Retention Period is the number of days for which automated backups are retained, by setting this parameter to a positive number you can enable backups backups, set it to 0 (zero) if you want to disable automated backups.
Database Subnet Group allows you to specify a particular VPC when you create DB instance. If you use the AWS web console, you can choose the VPC and subnets you want to use, each DB subnet group must have at least one subnet in at least two Availability Zones in the AWS Region to support Multi Availability Zone DB instance deployments.
AWS CloudFormation Template to Create Amazon RDS
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: This template creates an RDS database with MYSQL 5.7 engine
Metadata:
AWS::CloudFormation::Interface:
# In metadata key AWS::CloudFormation::Interface allows you to group parameters for displaying them
#on AWS CloudFormation console, so that users can efficiently specify parameter values
ParameterGroups:
-
Label:
default: Database Parameters
Parameters:
- DatabaseInstanceIdentifier
- DatabaseName
- DatabaseUser
- DatabasePassword
- DatabaseBackupRetentionPeriod
- DatabaseAllocatedStorage
- DatabaseInstanceClass
- MultiAZDatabase
Parameters:
# Give a name for database instance
DatabaseInstanceIdentifier:
AllowedPattern: '[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*'
ConstraintDescription: Can only contain alphanumeric characters and must begin with a letter
Default: mysql57db
Description: Instance identifier name
MaxLength: 60
MinLength: 1
Type: String
DatabaseName:
AllowedPattern: '[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*'
ConstraintDescription: Use alphanumeric characters only and must begin with a letter
Default: applicationdb
Description: MySQL database name
MaxLength: 64
MinLength: 1
Type: String
# In the below parameter declaration property NoEcho defines whether to mask the parameter value to
#prevent it from being displayed in the console.
DatabaseUser:
AllowedPattern: '[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*'
Default: dbadmin
Description: Username for MySQL database access
MaxLength: 16
MinLength: 1
NoEcho: true
Type: String
DatabasePassword:
AllowedPattern: '[a-zA-Z0-9]*'
ConstraintDescription: Must contain only alphanumeric characters
Default: database1407
Description: Password for MySQL database access
MaxLength: 41
MinLength: 8
NoEcho: true
Type: String
# DB backup retention period default value is set to 0 , this means backup is disabled.
DatabaseBackupRetentionPeriod:
ConstraintDescription: Database backup retention period must be between 0 and 35 days
Default: 0
Description: Give the number of days for which automatic Database snapshots are retained for bacckup
MaxValue: 35
MinValue: 0
Type: Number
DatabaseAllocatedStorage:
ConstraintDescription: Storage should be between 5 and 1024Gb
Default: 20
Description: Give size of the database in GB
MaxValue: 65536
MinValue: 5
Type: Number
DatabaseInstanceClass:
AllowedValues:
- db.t1.micro
- db.t2.micro
- db.m1.small
- db.m1.medium
- db.m1.large
ConstraintDescription: Please select a valid database instance type
Default: db.t2.micro
Description: The database instance type
Type: String
MultiAZDatabase:
AllowedValues:
- true
- false
ConstraintDescription: Must be either true or false
Default: false
Description: Creates a Multi-AZ MySQL Amazon RDS database instance
Type: String
Resources:
DatabaseSubnetGroup:
Type: AWS::RDS::DBSubnetGroup
Properties:
DBSubnetGroupDescription: Subnet group for RDS database
SubnetIds:
- subnet-02200c475327c5e49
- subnet-04dbbbfb9d2a57d30
- subnet-0a08ff4721f0fd58a
- subnet-0c025210cbbb349af
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: database subnets
DatabaseInstance:
Type: AWS::RDS::DBInstance
Properties:
AllocatedStorage: !Ref DatabaseAllocatedStorage
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 0, !GetAZs '' ]
BackupRetentionPeriod: !Ref DatabaseBackupRetentionPeriod
DBInstanceClass: !Ref DatabaseInstanceClass
DBInstanceIdentifier: !Ref DatabaseInstanceIdentifier
DBName: !Ref DatabaseName
DBSubnetGroupName: !Ref DatabaseSubnetGroup
Engine: MySQL
EngineVersion: 5.7.38
MasterUsername: !Ref DatabaseUser
MasterUserPassword: !Ref DatabasePassword
MultiAZ: !Ref MultiAZDatabase
VPCSecurityGroups:
- sg-01cb3f6971a0df2d7
- sg-0638ab478a46efc53
Launch RDS Instance using Cloud Formation
On you AWS web console open CloudFormation and click on Create Stack , In step-1 select Template is ready for prerequisite and choose template source
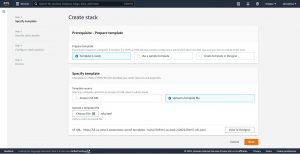
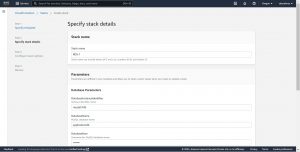
In step-2 give a name to your stack and you can also change the default parameter values here .
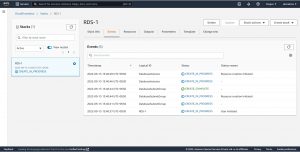
In step-3 configure your stack options like Roll back options, permissions, tags and in step-4 review your stack configuration and click on create to create the resources , you will be redirected to events page where you can see the progress of resources creation.
Connecting to Amazon RDS from a EC2 Instance
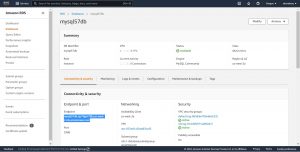
Once the resource is created successfully, go to RDS on your AWS console , and click on the Database Identifier name that you want to connect to, connecting to database on RDS is nothing new from accessing a remote database server it only varies based on the database engine you use.
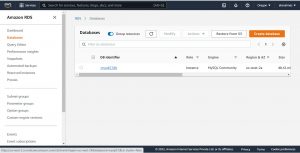
Copy the endpoint from Connectivity and Security and store it somewhere.
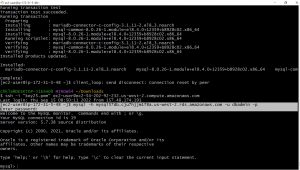
on you ec2 instance install MySQL client , you can following command on a Linux server.
sudo yum install mysql

use the following command to connect to the database, and enter the database password when it prompts for
mysql -h <database endpoint> -u <username> -p
Author Details:
This blog is written Amit Kumar, Director of Engineering at Checkmate Global TeTechnologies. You can please connect with to consult anything about product development, dedicated development team composition infrastructure management and DevOps engineering.


