Amazon Simple Storage Sevice(S3) is an object storage service provided by AWS. S3 stores data as objects in buckets. In Amazon S3, a storage class is associated with every object.
Storage Classes in Amazon S3:
- S3 Standard: It is the default storage class in Amazon S3. When you upload an object, Amazon S3 automatically assigns the S3 Standard storage class if you don’t specify another storage class.
- Reduced Redundancy: For non-critical, reproducible data that can be kept with less redundancy than the S3 Standard storage class, the Reduced Redundancy Storage (RRS) storage class is used.
- S3 Intelligent-Tiering: S3 Intelligent-Tiering is an Amazon S3 storage class created to save operational costs and storage costs by automatically transferring data to the most economical access tier. A Frequent Access tier, an Infrequent Access tier, and an Archive Instant Access tier are the three access tiers that S3 Intelligent-Tiering automatically stores things in. Objects that are stored in S3 intelligent-tiering will by default be stored in the Frequent Access tier. When an item hasn’t been accessed for 30 days in a row, S3 Intelligent-Tiering monitors access patterns and moves it to the Infrequent Access tier. Any existing items that haven’t been accessed for 90 days straight will automatically shift to the Archive Instant Access tier thanks to S3.
- S3 Standard-Infrequent Access: S3 Standard-IA is used for data that is accessed infrequently but yet needs quick access on occasion. S3 Standard-IA provides the high throughput, low latency, and great durability of S3 Standard at a reasonable cost per GB of storage and retrieval. The object data is redundantly stored by Amazon S3 across various Availability Zones
- S3 One Zone-IA: Amazon S3 One Zone-IA is less expensive than S3 Standard-IA since it only stores the object data in one Availability Zone. S3 One Zone-IA storage class is less accessible and less resilient than Standard-IA.
- S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval: S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval is used for archiving data that needs to be retrieved in milliseconds but is rarely accessed. With the same latency and throughput performance as the S3 Standard-IA storage class, data saved in the S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval storage class is less expensive than data stored in the S3 Standard-IA storage class.
- S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval: It is used for archives where some of the data might need to be retrieved in minutes. With expedited retrieval, data saved in the S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval storage class can be accessible in as little as 1–5 minutes and has a minimum storage duration term of 90 days.
- S3 Glacier Deep Archive: It is used for archiving data that rarely needs to be accessed. Data saved in the S3 Glacier Deep Archive storage class has a default retrieval time of 12 hours and a minimum storage retention period of 180 days.
S3 Lifecycle Policy
S3 Lifecycle Policy is a set of rules or configurations that define actions that Amazon S3 applies to the objects. These policies manage objects so that they are stored cost-effectively throughout their lifecycle.
There are two types of action that Amazon S3 applies:
- Transition actions: These actions specify when an object changes from one storage class to another. For example, you may want to move an object to the S3 Standard-IA storage class 30 days after creating them, in that case, we use transition action.
- Expiration actions: These actions specify when an object is to be expire and deleted. Amazon S3 deletes the expired objects itself.
Steps to create Lifecycle Rules:
- Go to S3 Console->Bucket. Select your bucket.
- Select your bucket and go to Management.
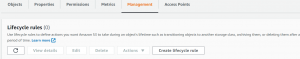
- Click Create lifecycle rule.
- Give a name to rule. We can select if we want to apply the rule to all objects in the bucket or limit it to certain objects.
- We will only apply the rule to objects in one folder. Select the rule scope as Limit the scope of this rule using one or more filters and enter folder name prefix as a filter.
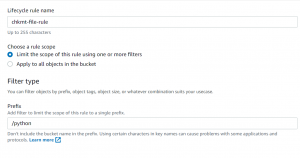
- We can use Object Tags and Object Size as filters as well to limit the scope of lifecycle rules to certain objects.

- Next, we can select the Lifecycle rule actions.
- We will select the action such that the current version of the object will move between storage classes and will be expired.
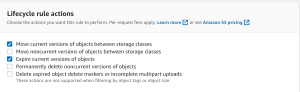
- Next, select the storage class and the number of days for which the object will remain in that storage class.
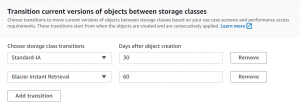
- Here we have created a rule that our object will move to Standard-IA storage class 30 days after creation, and after the next days, it will move to Glacier Instant Retrieval class.
- Now select the number of days after which the object will get expire.
- Review the rule and click Create Rule.

- We have created the lifecycle rule for the objects in the S3 bucket.
Please contact our DevOps Manager to know more about AWS cloud infrastructure best practices. We can help hire best AWS cloud engineer.


