Note: This blog assumes that you already know how to create a VPC using AWS web console and have a clear understand of it’s architecture and requirements, if you are new to Cloud Formation please refer this blog for basic understand of what it is.
What are Parameters, Resources, Outputs in an AWS Cloud Formation template?
Parameters
when you want to allow any user input while creating a stack like name of a s3 bucket or if you want to reuse the same template it’s not recommended to hardcode all the details of your resources rather you can give these details using parameters, let’s see this while creating the stack in aws console, and it’s completely optional to define parameters in a template , below is an example parameter which is intended to be used for a VPC CIDR.
Parameters:
VpcCIDR:
Default: 10.0.0.0/16
Description: Please enter the CIDR (IP range) for this VPC
Type: String
all the parameters that you declare in a template should be under Parameters: tag only and VpcCIDR: is the logical names it can be any alpha alphanumeric value and it should be unique from all the logical names that were defined with in a template as one can refer to this parameter with this logical name only, different parameter types allowed string , number, list of numbers, comma-delimited list , the type of value allowed for a particular parameter is declared under Type:, and the value given for Default: key word will be used by cloud formation for creating the stack/infrastructure if no other value is given by the user while creating the stack.
Resources
there more than 200 plus resources available in aws , the infrastructure that you want to deploy should be declared under Resources tag in configuration file , and every resource will have its own properties and there will be some required properties for each resource that need to be declared to deploy a resource, below is the basic syntax to declare a resource
Resources:
VPC:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC
Properties:
CidrBlock: !Ref VpcCIDR
EnableDnsHostnames: true
EnableDnsSupport: true
InstanceTenancy: default
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: Test VPC
Here Resources: is tag under which you need to declare resources that you want deploy and Type:AWS::EC2::VPC is the resource key word for VPC . CidrBlock, EnableDnsHostnames, InstanceTenancy are the basic properties that are needed to create a vpc, and as you can see Intrinsic function !Ref is used to get the value for CidrBlock property by referring to VpcCIDR which is declared in Parameters part.
Intrinsic functions are basically built-in functions that comes within the AWS cloud formation, The intrinsic function Ref returns the value of the given parameter or resource, when you specify a parameter’s logical name, it returns the value of the parameter and if you specify a resource’s logical name, it returns a value that you can use to refer to that resource.
Outputs
once the stack is created or the infrastructure is deployed to get the details of resources , for example you have deployed a ec2 instance and you want Id of that instance you have to go all the way to ec2 dashboard in AWS web console for this , to make it easier we can declare outputs with in the same template you are using to create your infrastructure , this will give you specific details in the output section of cloud formation, lets see this while creating the stack in CF.
below is the basic syntax to declare a output ,
Outputs:
Logical ID:
Description: Information about the value
Value: Value to return
Export:
Name: Name of resource to export
Intrinsic Function in AWS Cloud Formation
Before going on to create whole template to create a VPC Let’s look in to two more intrinsic functions.
!Sub
The intrinsic function Fn: :Sub called as substitute function substitutes variables in an input string with values that you specify, you can use this function to construct commands or outputs in your template, go through the below given yaml configuration and explanation below it.
Resources:
VPC:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC
Properties:
CidrBlock: !Ref VpcCIDR
EnableDnsHostnames: true
EnableDnsSupport: true
InstanceTenancy: default
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: Test VPC
Outputs:
VPC:
Description: VPC ID
Export:
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-VPC
Value: !Ref VPC
In the above cloud formation template, Fn:: Sub is used in the output to give a export name, ${Variable name } this is the syntax to describe a variable using substitute function, !Sub ${AWS::StackName} is used it to get the stack name and giving it as a Export name.
GetAZs
The intrinsic function Fn::GetAZs returns an array that lists Availability Zones in a region in alphabetical order, so that way you don’t have to hard-code a full list of Availability Zones for a specified region.
Select intrinsic function select returns a single object from a list of objects based on given index.
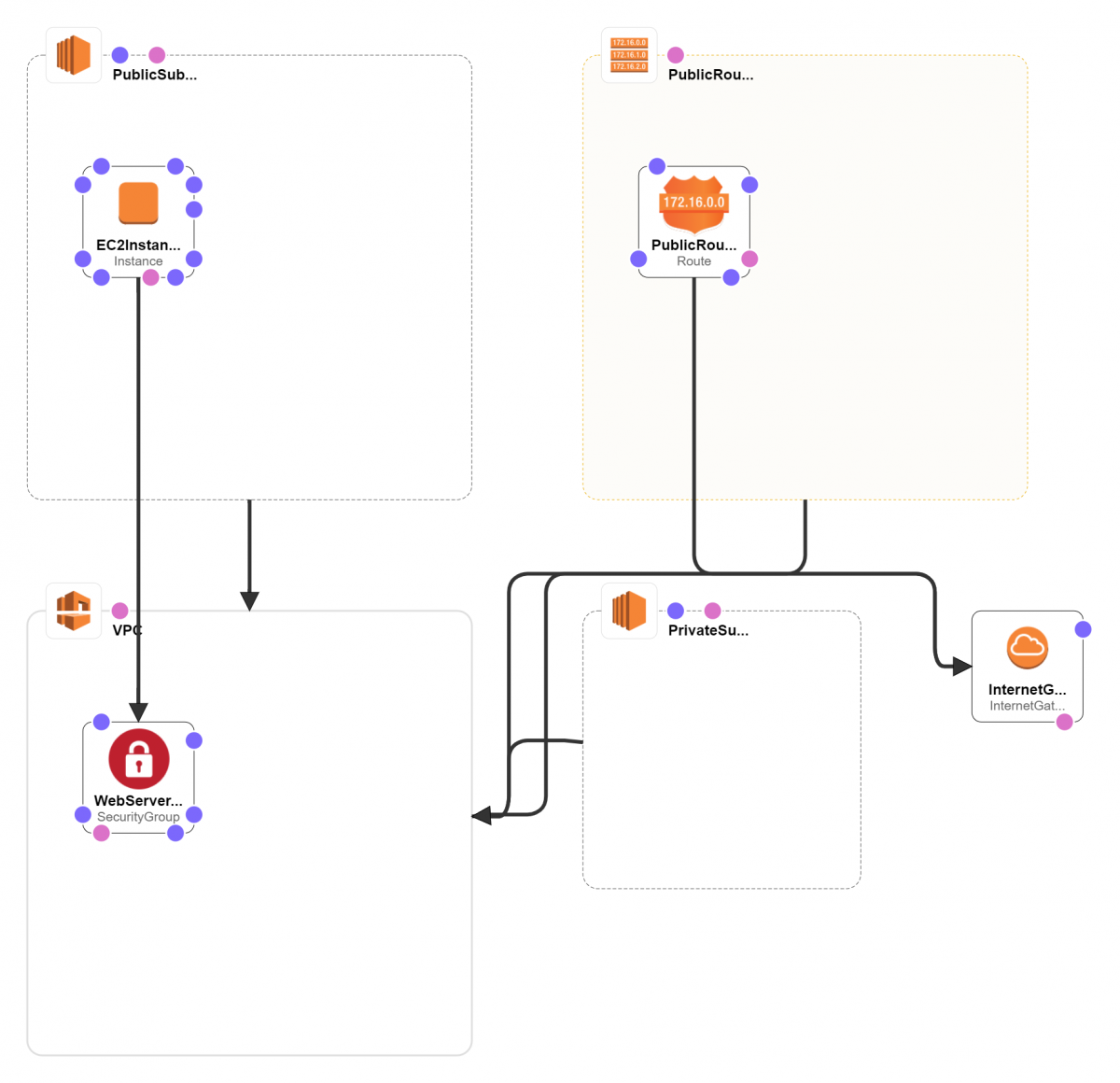
Cloud Formation Template to Create VPC
Below is the complete configuration in yaml for creating a VPC(CIDR: 10.0.0.0/16 ) with one public (CIDR: 10.0.0.0/24) and one private subnet(CIDR: 10.0.1.0/24), go through each block and save in a yaml file.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: This template creates vpc with public and private subnets
# Parameters are used to to build flexible/reusable CloudFormation templates
Parameters:
VpcCIDR:
Default: 10.0.0.0/16
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for this VPC
Type: String
PublicSubnet1CIDR:
Default: 10.0.0.0/24
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the public subnet 1
Type: String
PrivateSubnet1CIDR:
Default: 10.0.2.0/24
Description: Please enter the IP range (CIDR notation) for the private subnet 1
Type: String
SSHLocation:
Default: 0.0.0.0/0
Description: The IP address range that can be used to access the web server using SSH.
MaxLength: '18'
MinLength: '9'
Type: String
Resources:
# Create VPC
VPC:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC
Properties:
CidrBlock: !Ref VpcCIDR
EnableDnsHostnames: true
EnableDnsSupport: true
InstanceTenancy: default
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: Test VPC
# Create Internet Gateway
InternetGateway:
Type: AWS::EC2::InternetGateway
Properties:
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: Test IGW
# Attach Internet Gateway to VPC
InternetGatewayAttachment:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment
Properties:
InternetGatewayId: !Ref InternetGateway
VpcId: !Ref VPC
# Create Public Subnet1
PublicSubnet1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 0, !GetAZs '' ]
CidrBlock: !Ref PublicSubnet1CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: Public Subnet 1
VpcId: !Ref VPC
# Create Route Table
PublicRouteTable:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: Public Route Table
VpcId: !Ref VPC
# Add a Public Route to the Route Table
PublicRoute:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
Properties:
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
GatewayId: !Ref InternetGateway
RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable
# Associate Public Subnet1 with Public Route Table
PublicSubnet1RouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet1
# Create Private Subnet1
PrivateSubnet1:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
AvailabilityZone: !Select [ 0, !GetAZs '' ]
CidrBlock: !Ref PrivateSubnet1CIDR
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: false
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: Private Subnet 1 | App Tier
VpcId: !Ref VPC
# Create Security Group for the Web Server
WebServerSecurityGroup:
Type: 'AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup'
Properties:
GroupDescription: Enable traffic on ports 80/http, 443/https, 22/SSH
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: '80'
ToPort: '80'
CidrIp: "0.0.0.0/0"
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: '443'
ToPort: '443'
CidrIp: "0.0.0.0/0"
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: '22'
ToPort: '22'
CidrIp: "0.0.0.0/0"
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: WebServer Security Group
VpcId: !Ref VPC
#Create an EC2 instance in public subnet.
EC2Instance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
InstanceType: t2.micro
ImageId: "ami-051dfed8f67f095f5"
KeyName: key9
NetworkInterfaces:
- DeviceIndex: 0
AssociatePublicIpAddress: true
DeleteOnTermination: true
SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnet1
GroupSet:
- !Ref WebServerSecurityGroup
Outputs:
# Export VPC ID
VPC:
Description: VPC ID
Export:
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-VPC
Value: !Ref VPC
# Export Public Subnet 1
PublicSubnet1:
Description: Public Subnet 1 ID
Export:
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-PublicSubnet1
Value: !Ref PublicSubnet1
# Export Private Subnet 1
PrivateSubnet1:
Description: Private Subnet 1 ID
Export:
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-PrivateSubnet1
Value: !Ref PrivateSubnet1
# Export WebServer Security Group ID
WebServerSecurityGroup:
Description: Webserver Security Group ID
Export:
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-WebServerSecurityGroup
Value: !Ref WebServerSecurityGroup
# Export DataBase Security Group ID
EC2Instance:
Description: EC2 Instance ID
Export:
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-EC2Instance
Value: !Ref EC2Instance
Steps to Create Infrastructure using Cloud Formation and Configuration Template
On your AWS web console search for Cloud Formation then click on create stack.
Stack: To create resources defined in template you need to create a stack in cloud formation which allows you to manage your resources like delete update or create.
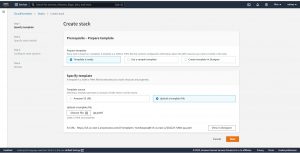
Then in step-2 give a name to your stack and also you change the default values of the parameters that you declared in the configuration template.
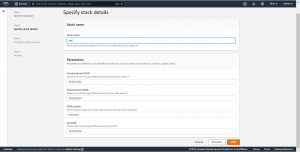
In step-3 you can give tags and the IAM role that should be used by CF to create your stack and in Step-4 Review all the details and click on Create Stack , this will redirect you to events page where you can see the progress of the deployment.
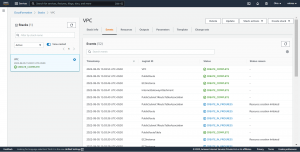
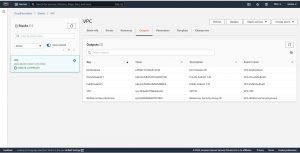
Now go to Outputs to see the values that you have exported in the configuration file.
Please contact our cloud consultants if you have any cloud infrastructure related issues to be discussed.