Ansible is a configuration management tool for used to automation, system configuration management, package management, automate provisioning operations and handle more complex SRE management operations such as automated infrastructure deployment, patch management, server reboot sanitary checks, OS upgrades and package deployment, with pre-defined YAML language written playbook. Ansible can be easily integrated with Jenkins release pipeline as part of continuous integration or continuous deployments pipeline.
In this Ansible blog, we use ansible to create a Kubernetes cluster on AWS cloud EC2 instances. We will create 1 control node and 2 worker nodes. We will install all the packages and dependencies using ansible playbooks.
Prerequisites:
- Host server running with Ansible installed.
- ssh-key pair set up to connect to Kubernetes master and worker nodes.
Step1: Setup inventory file
- Add master and worker nodes in the hosts file.
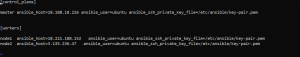
- Ping all nodes to make sure you can connect to them.
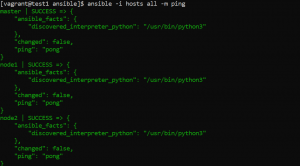
Ste2: Set up a user on nodes
- Next, we will set up a non-root user with sudo permissions on the master and worker nodes so that we can manage the cluster safely.
- Create an ansible playbook and copy the following code there.
- hosts: all
become: yes
tasks:
- name: create the 'k8sadmin' user
user:
name: k8sadmin
append: yes
state: present
createhome: yes
shell: /bin/bash
- name: allow 'k8sadmin' sudo permission
lineinfile:
dest: /etc/sudoers
line: 'k8sadmin ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL'
validate: 'visudo -cf %s'
- name: set authorized keys for the k8sadmin user
authorized_key:
user: k8sadmin
key: "{{item}}"
with_file:
- ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
- Run this playbook to create users on all remote nodes.
Step3: Install CRI-O runtime and other Kubernetes dependencies on all nodes
- Create a playbook for installing dependencies and paste the following code there.
- hosts: all
become: yes
become_user: root
gather_facts: yes
tasks:
- name: Create CRI-O config file
file:
path: "/etc/modules-load.d/crio.conf"
state: "touch"
- name: add modules in conf file
blockinfile:
path: "/etc/modules-load.d/crio.conf"
block: |
overlay
br_netfilter
- name: Enable sysctl params
file:
path: "/etc/sysctl.d/99-kubernetes-cri.conf"
state: "touch"
- name: add configuration
blockinfile:
path: "/etc/sysctl.d/99-kubernetes-cri.conf"
block: |
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
- name: enable overlayFS & VxLan pod communication
shell: |
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
- name: Reload parameters
command: sudo sysctl --system
- name: disable swap
shell: |
sudo swapoff -a
sudo sed -i '/ swap / s/^\(.*\)$/#\1/g' /etc/fstab
- name: enable cri-repo
environment:
OS: xUbuntu_20.04
VERSION: 1.23
shell: |
echo "deb https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:/kubic:/libcontainers:/stable/$OS/ /" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/devel:kubic:libcontainers:stable.list
echo "deb http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:/kubic:/libcontainers:/stable:/cri-o:/$VERSION/$OS/ /" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/devel:kubic:libcontainers:stable:cri-o:$VERSION.list
curl -L https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:kubic:libcontainers:stable:cri-o:$VERSION/$OS/Release.key | apt-key add -
curl -L https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:/kubic:/libcontainers:/stable/$OS/Release.key | apt-key add -
- name: Install cri-o and cri-o tools
shell: |
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install cri-o cri-o-runc cri-tools -y
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable crio --now
- name: Install dependencies
shell: |
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https curl
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
- name: Create kubernetes repo file
file:
path: "/etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list"
state: "touch"
- name: Add K8s Source
blockinfile:
path: "/etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list"
block: |
deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main
- name: install kubernetes
shell: |
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet=1.23.1-00 kubeadm=1.23.1-00 kubectl=1.23.1-00
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Step4: Initialize kubeadm on the master node
- Next we will initialize the cluster using kubeadm init command on contrrol plane.
- Then we will print the join yoken and copy it to ansible host.
- hosts: master
become: yes
tasks:
- name: initialize the cluster
shell: sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=192.168.0.0/16 --cri-socket=/var/run/crio/crio.sock --ignore-preflight-errors Swap >> cluster_initialized.txt
args:
chdir: $HOME
creates: cluster_initialized.txt
- name: create .kube directory
become: yes
become_user: k8sadmin
file:
path: /home/k8sadmin/.kube
state: directory
mode: 0755
- name: copy admin.conf
copy:
remote_src: yes
src: /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
dest: /home/k8sadmin/.kube/config
owner: k8sadmin
- name: Install calico Pod network
become: yes
become_user: k8sadmin
shell: kubectl apply -f https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/calico.yaml
args:
chdir: $HOME
- name: Get join token
become: yes
become_user: k8sadmin
shell: sudo kubeadm token create --print-join-command
register: kubernetes_join_command
- name: Copy join command to local file.
become: yes
local_action: copy content="{{ kubernetes_join_command.stdout_lines[0] }}" dest="/tmp/kubernetes_join_command" mode=0777
Step4: Set up worker nodes
- Now we will copy the join command to worker nodes from the ansible host and execute it.
- hosts: workers
become: yes
gather_facts: yes
tasks:
- name: Copy join command from Ansiblehost to the worker nodes.
become: yes
copy:
src: /tmp/kubernetes_join_command
dest: /tmp/kubernetes_join_command
mode: 0777
- name: Join the Worker nodes to the cluster.
become: yes
command: sh /tmp/kubernetes_join_command
register: joined_or_not
- Now ssh to the master node and verify that nodes are ready.
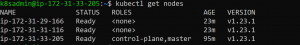
Author Details
This blog is Written by Amit Kumar, Head of Engineering, at Checkmate Management Consulting. Please reach to him for Cloud engineering infrastructure best practices, Hire Software Developer in India, IT Staff Augmentation Services, Remote Virtual CTO Services and infuse cloud support best practices to stable daily production operation and Technology Consulting Services.


