The objective of a HorizontalPodAutoscaler in Kubernetes is to automatically scale the workload to match demand by updating a workload resource such as a Deployment or StatefulSet. When a load increases, more Pods are deployed, which is referred to as horizontal scaling. The HorizontalPodAutoscaler informs the workload resource (the Deployment, StatefulSet, or other similar resources) to scale back down if the load drops and the number of Pods is more than the defined minimum.
For using horizontal pod autoscaler in Kubernetes first we will need to install the Kubernetes metric server which queries the resource usages of pods and nodes like CPU and memory utilization.
For installing the metric server in EKS use the following commands.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml kubectl get deployment metrics-server -n kube-system
If you’re using any local Kubernetes cluster like minikube then you will need to add the –kubelet-insecure-tls argument in the container property in the metrics server deployment manifest file.
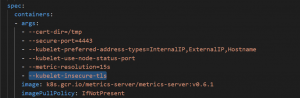
Use the following command to verify that the metrics server deployment is running.
kubectl get deployment metrics-server -n kube-system

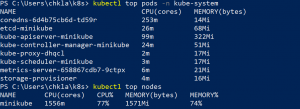
Now we will deploy an Nginx web server using Kubernetes deployment. To use the autoscaler we will need to define the resource requests. Requests define the minimum amount of resources required by pods.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deploy
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: web
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: web
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.23
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
memory: 200Mi
cpu: 100m
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: web
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
nodePort: 30080
Next, deploy the horizontal pod autoscaler manifest file. Here we have defined that if CPU usage increase above 50, it will scale up the replicas.
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: nginx-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx-deploy
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
behavior:
scaleDown:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 60
policies:
- type: Pods
value: 1
periodSeconds: 60
scaleUp:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 0
policies:
- type: Pods
value: 2
periodSeconds: 15
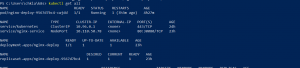
Now for testing the autoscaler, we will use a busybox container deployment. It will call the Nginx pods in a loop and hence increase the CPU load.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-load
labels:
app: nginx-load
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-load
template:
metadata:
name: nginx-load
labels:
app: nginx-load
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- "while true; do wget -q -O- nginx-service; done"
After deploying the busybox pod we will see that CPU utilization will increase. In our case it has increased up to 80% which is above 50% threshold that we defined.
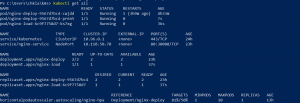
After some time, autoscaler will notice the increased CPU utilization and increase the number of replicas up to 3, thus bringing down the CPU utilization.
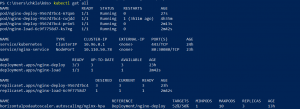
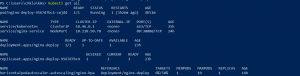
Now we will delete the busy box deployment and we will see that in some time number of replicas will scale down as well.
Author Details
This post is written by Amit Kumar, Engineering Director, Checkmate Global Technologies. Please contact him for if you have anything related to cloud infrastructure to be discussed.


